Connecting the Dots: EMRs and the Evolution of Canadian Healthcare
How EMRs can finally send the fax machine into retirement and transform Canadian healthcare.
In today’s increasingly digital world, the way healthcare providers manage patient information can make or break the quality of care delivered. At the heart of this transformation lies the Electronic Medical Record (EMR)—a system that replaces cumbersome paper files with streamlined, digitized records. But why are EMRs so critical in the first place?
The answer lies in their potential to not only store patient data but also to enable better decision-making, enhance collaboration between healthcare providers, and improve outcomes for patients. In Canada, where healthcare systems often face challenges with accessibility, efficiency, and communication, EMRs hold the promise of a more connected and patient-centered future.
Primary and acute care providers, highly trained professionals who are adept at using up-to-date technology to help look after patients, still rely heavily on a distinctly 20th-century device: the fax machine. (Source: CTV News)
This article delves into the importance of EMR systems, the barriers preventing them from reaching their full potential, and how innovation in this space can shape the next era of healthcare in Canada.
It’s also the first in a four-part series exploring EMRs:
• This Week: Digital Health EMR Systems in Canada
• Next Week: Provincial EMR Systems – Compared
• Week After: EMR Companies in Canada and Rising Startups
• Final Week: Digital Health Privacy
The Current Landscape of EMRs in Canada
Electronic medical records have transformed the way patient information is stored and accessed. Gone are the days of cumbersome paper files; today, most patient data is digitized. However, despite this progress, significant challenges remain. According to a report by the Competition Bureau Canada, the lack of interoperability between different EMR systems is a major barrier. This means that while data is stored electronically, it often cannot be easily shared across different healthcare providers or systems.
Key Challenges:
Interoperability Issues: Many EMR systems cannot communicate with each other, hindering the seamless exchange of patient information.
Market Dominance: A few companies dominate the EMR market in Canada, making it difficult for new entrants to introduce innovative solutions.
Data Accessibility: Patients and healthcare providers face challenges in accessing and sharing personal health information securely and efficiently.
The Importance of Competition and Innovation
The Competition Bureau's report emphasizes the need for increased competition in the digital healthcare sector. By facilitating secure access and sharing of health data, Canada can create a more competitive environment that encourages innovation. This is crucial for the development of new digital health solutions, such as e-pharmacy platforms, virtual care, and mobile health apps.
Recommendations for Enhancing Competition:
Policy Reforms: Implementing policies that promote data sharing while ensuring privacy and patient consent.
Encouraging New Entrants: Reducing barriers for startups and innovators to enter the market with cutting-edge solutions.
Fostering Interoperability: Developing standards that ensure different EMR systems can communicate effectively.
The Role of EMRs in Research and Development
Beyond improving patient care, EMRs offer a wealth of data that can be harnessed for research purposes. As highlighted in a study by Richard Birtwhistle and Tyler Williamson, EMRs provide a "laboratory" for primary care research. By aggregating data from multiple practices, researchers can gain insights into healthcare delivery at regional, provincial, and national levels.
Research Opportunities:
Chronic Disease Management: EMR data can be used to study the management of chronic diseases like diabetes and hypertension.
Predictive Analytics: By linking EMR data with other datasets, researchers can develop predictive models to identify risk factors for chronic diseases.
Health System Evaluation: EMR data can be used to evaluate and monitor health systems, identify gaps in care, and develop interventions to improve patient outcomes.
The Future of Health Data in Canada
The Shared Pan-Canadian Interoperability Roadmap outlines a vision for creating a connected and equitable health system across Canada. By addressing key challenges like data silos, poor interoperability between systems, and limited patient access to records, this roadmap aims to modernize healthcare delivery. It emphasizes standardizing health data, fostering collaboration among provinces, and leveraging innovative technologies to improve care coordination, reduce inefficiencies, and enhance patient outcomes. This initiative highlights the critical role of interoperability in advancing Canada’s healthcare system into a more integrated and patient-centered future.
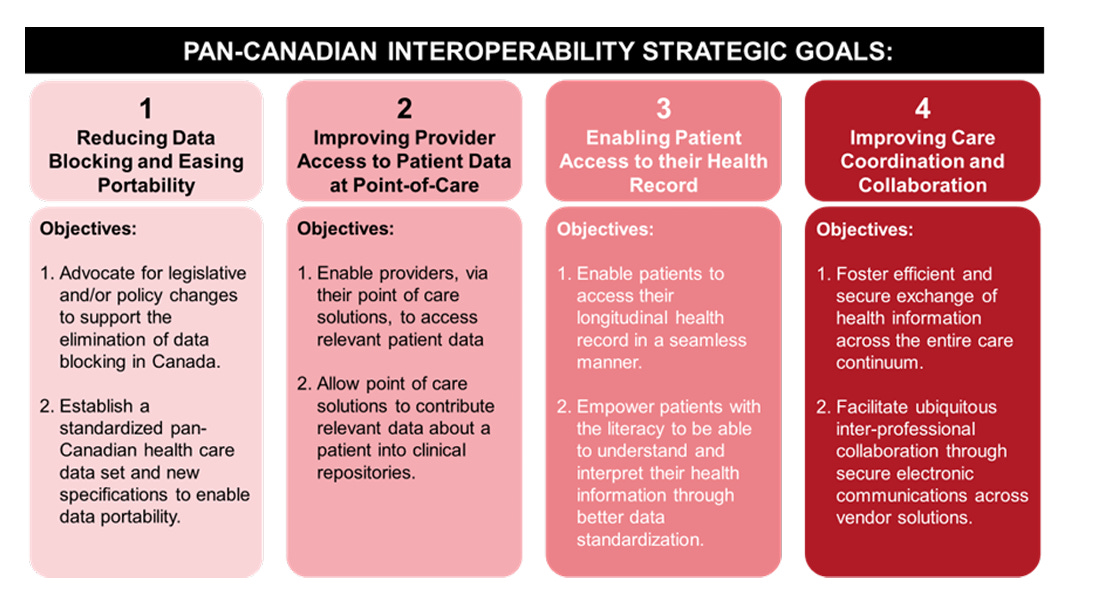
Key Takeaways:
Collaboration is Key: Stakeholders across the healthcare and tech sectors must work together to overcome existing barriers.
Patient-Centric Solutions: Innovations should focus on enhancing patient care and ensuring data privacy and security.
Continuous Improvement: As technology evolves, so too must the systems and policies governing health data.
The future of Canadian healthcare is intricately tied to how we leverage electronic medical records. By addressing key challenges like interoperability and market competition, EMRs can unlock new opportunities for innovation, enhance patient care, and create a more cohesive healthcare ecosystem. However, this transformation requires collaboration among policymakers, healthcare providers, and tech innovators to ensure these systems are efficient, secure, and centered on the needs of patients.
This article is just the beginning of our four-part series exploring EMRs in Canada. Over the next few weeks, we’ll dive deeper into:
• Part Two: Provincial EMR Systems – Compared
• Part Three: EMR Companies in Canada and Rising Startups
• Part Four: Digital Health Privacy
Stay with us as we explore the critical role EMRs play in shaping the future of healthcare in Canada.
References
Birtwhistle, R., & Williamson, T. (2015). Primary care electronic medical records: A new data source for research in Canada. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4347766/
Competition Bureau Canada. (2022). Unlocking the power of health data. Retrieved from https://competition-bureau.canada.ca/unlocking-power-health-data
CTV News. (2024). What am I supposed to do with these CD-ROMs? The benefits and challenges of implementing electronic medical records in Canada. Retrieved from https://www.ctvnews.ca/health/what-am-i-supposed-to-do-with-these-cd-roms-the-benefits-and-challenges-of-implementing-electronic-medical-records-in-canada-1.6993517
Infoway, Canada Health. (2023). Connecting you to modern health care: Shared pan-Canadian interoperability roadmap. Retrieved from https://www.infoway-inforoute.ca/en/component/edocman/resources/interoperability/6444-connecting-you-to-modern-health-care-shared-pan-canadian-interoperability-roadmap?Itemid=101
Read Our First Article & Share Your Ideas
If you missed it, be sure to check out our first article here, where we covered key reasons why we started our Canadian Health Tech newsletter.
We’d also love to hear from you! What topics would you like us to explore next? Reply to this email or leave a comment with your suggestions – we’re always looking to provide valuable insights based on what matters to you.
We’ll continue to keep you informed about the latest developments and their impact on healthcare and tech in Canada. Stay tuned for more updates, and feel free to share your thoughts or questions with us!









