Wearing the Future: Why Wearable Tech is More Than Just a Trend in Canadian Healthcare
Can Wearables Close Canada’s Healthcare Gap and Empower Patients Nationwide?
Wearable Tech: Transforming Canadian Healthcare
The integration of wearable technology into healthcare has immense potential in how patients and providers interact with health data. In Canada, where healthcare accessibility can be limited by vast geographical distances, wearables present an opportunity to bridge gaps in care and empower patients with real-time health insights. From fitness trackers to medical-grade remote monitoring devices, these technologies are enhancing preventative care, early detection, and chronic disease management. As the market for wearable health technology expands, Canada must focus on accessibility, data security, and integration into clinical workflows to maximize its potential impact.
Empowering Patients with Data
Wearable technology in healthcare is revolutionizing patient experiences by empowering individuals with detailed health data that can lead to actionable insights. According to a report by Built In, wearables enable patients to collect their own health data and report it digitally, reducing the need for in-person appointments.
This capability is particularly beneficial in a country like Canada, where vast geographical distances can make regular healthcare visits challenging. By facilitating remote monitoring, wearables can help bridge the gap between patients and healthcare providers, ensuring continuous care and timely interventions.
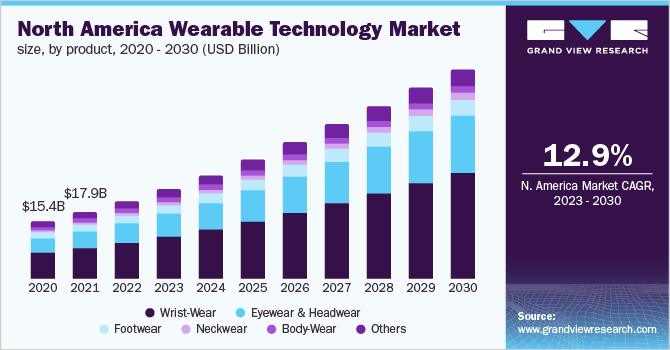
Market Growth and Leading Companies
The market for smart wearable health devices is booming, with projections indicating growth from $13.8 billion in 2020 to $37.4 billion by 2028. This surge is driven by the increasing demand for devices like fitness trackers, smartwatches, ECG monitors, and biosensors.
Companies such as Silvertree, Garmin, and Withings are at the forefront of this growth, offering innovative solutions that enhance the patient experience. For instance, Silvertree's Reach wristband is designed to monitor health and safety for older adults, promoting independence while providing emergency notifications and GPS tracking.
A report from Grand View Research suggests the global wearable technology market was valued at $61.3 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a 14.6% CAGR from 2023 to 2030, driven by increasing adoption of smart health-monitoring devices. The wrist-wear segment led the market, with consumer electronics being the dominant application.
North America held the largest share (33.8%), while Asia Pacific is projected to grow the fastest. Major players like Fitbit, Samsung, and Xiaomi continue to expand product offerings with health-tracking and AI-integrated features. The market’s growth is fueled by rising health awareness, technological advancements, and competitive pricing. For more information on this report, visit their website.
Medical Grade Wearables in Clinical Settings
In addition to consumer-grade wearables, medical-grade devices are gaining traction for their ability to support clinical decision-making. A study published in HealthTech Magazine highlights the role of wearables in remote patient monitoring, particularly for chronic conditions like diabetes and hypertension. These devices undergo rigorous clinical research and must receive regulatory clearance, ensuring their reliability and accuracy in healthcare settings.
Overcoming challenges requires investment in up-skilling healthcare professionals, particularly in data analysis, and addressing issues related to device usability and accessibility.
Canadian Innovators
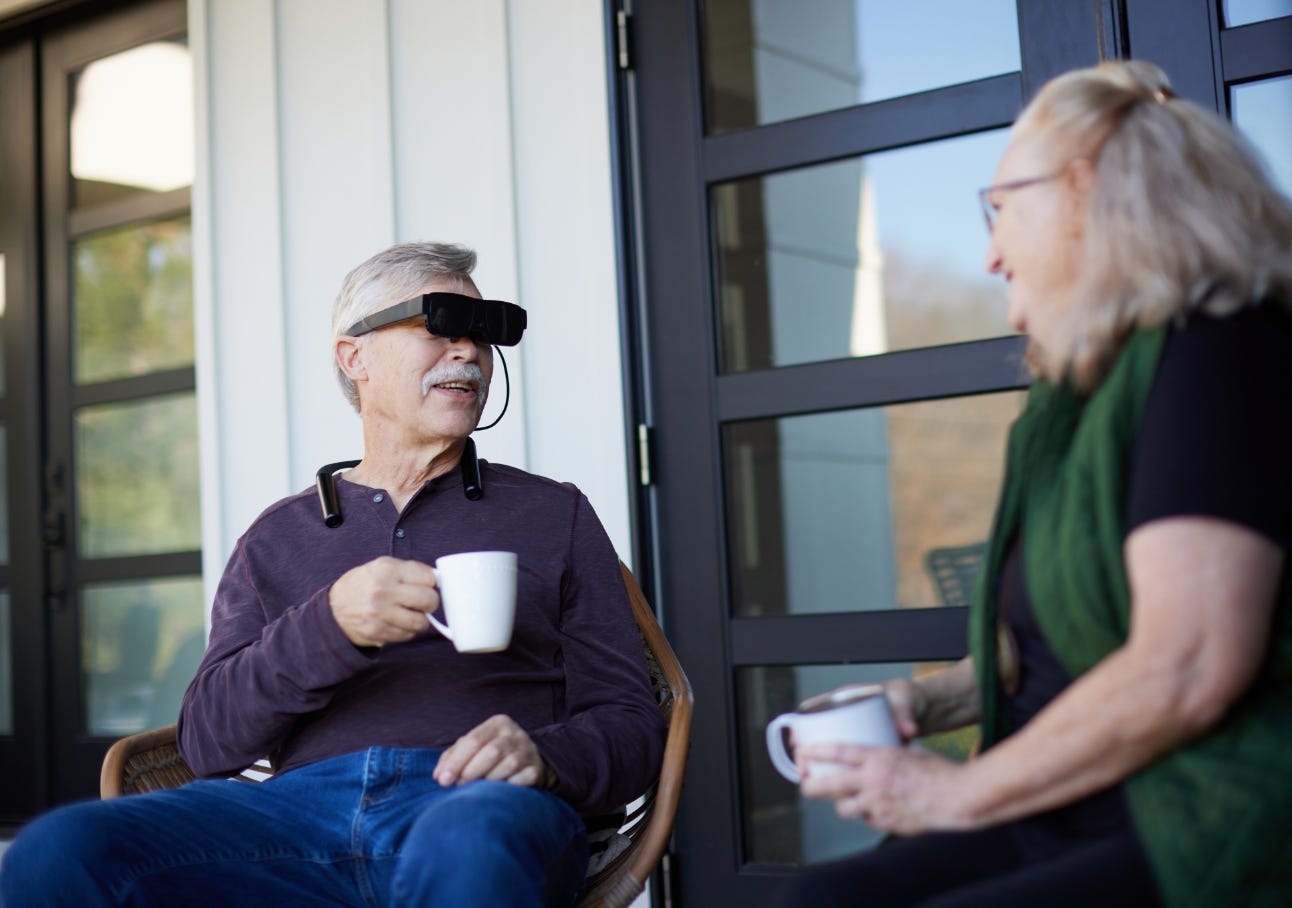
There are many companies in Canada that are contributing to the wearables market. For example, eSight is a Canadian company that develops advanced electronic eyewear designed to enhance vision for individuals with significant central vision loss. Their devices, such as the eSight 4, utilize a high-speed, high-definition camera to capture live video, which is then processed through proprietary algorithms and displayed on two OLED screens in front of the user's eyes. This technology assists individuals with conditions like macular degeneration and diabetic retinopathy in achieving improved visual acuity, enabling them to engage more fully in daily activities.
Muse, developed by Toronto-based InteraXon, is a brain-sensing headband designed to assist users in meditation and stress management. Utilizing electroencephalography (EEG) sensors, Muse monitors brain activity and provides real-time audio feedback through a companion mobile app, helping users achieve a more focused and relaxed state. The device also tracks heart rate, breath, and body movements, offering comprehensive insights into one's physiological state.
Challenges and Considerations
However, the integration of wearable technology into healthcare is not without challenges. A scoping review by Harjeevan Singh Kang and Mark Exworthy identifies potential barriers to the widespread adoption of wearables, including device accuracy, user engagement, and the need for healthcare providers to promote their use. Moreover, the ethical and technical considerations surrounding wearable technology are critical.
A study by Stefano Canali and colleagues emphasizes the importance of data quality, interoperability, and health equity in the deployment of wearables. Ensuring that devices are accessible to diverse populations and that data is used ethically and securely is paramount for the success of wearable technology in healthcare.
The Future of Wearable Technology in Canada
In Canada, the potential of wearable technology to enhance healthcare delivery is immense. By providing real-time data and facilitating remote monitoring, wearables can improve patient outcomes and reduce the burden on healthcare systems.
For healthcare professionals, these devices offer a more comprehensive view of patient health, enabling more informed and personalized care plans.
To fully realize the benefits of wearable technology, collaboration between healthcare providers, technology developers, and policymakers is essential. By fostering a supportive ecosystem, Canada can lead the way in integrating wearables into healthcare, ultimately improving the quality of care for all Canadians.
As the market continues to grow, the focus must remain on ensuring that these technologies are accessible, reliable, and beneficial for both patients and healthcare providers.
References
Built In. (2024). Wearable technology in healthcare. Retrieved from https://builtin.com/articles/wearable-technology-in-healthcare
Silvertree. (2025). Retrieved from https://silvertree.io/
Garmin. (2025). Retrieved from https://www.garmin.com/en-US/
Withings. (2025). Retrieved from https://www.withings.com/us/en/
HealthTech Magazine. (2024). Trends in wearable technology for healthcare. Retrieved from https://healthtechmagazine.net/article/2024/03/trends-wearable-technology-for-healthcare-perfcon
Kang, H. S., & Exworthy, M. (2022). Wearing the Future—Wearables to Empower Users to Take Greater Responsibility for Their Health and Care: Scoping Review. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9330198/
Canali, S., et al. (2022). Challenges and recommendations for wearable devices in digital health: Data quality, interoperability, health equity, fairness. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9931360/
Grand View Research. (2023). Wearable Technology Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report By Product (Head & Eyewear, Wristwear), By Application (Consumer Electronics, Healthcare), By Region (Asia Pacific, Europe), And Segment Forecasts, 2023 - 2030. Retrieved from https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/wearable-technology-market.
Esight (2025). Retrieved from https://www.esighteyewear.com/
Muse (2025). Retrieved from https://choosemuse.com/